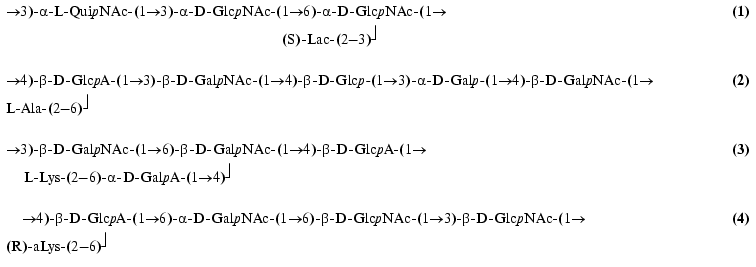New Structures of the O-Specific Polysaccharides of Proteus. 3. Polysaccharides Containing Non-carbohydrate Organic Acids
A. N. Kondakova1, F. V. Toukach1, S. N. Senchenkova1, N. P. Arbatsky1, A. S. Shashkov1, Y. A. Knirel1*, B. Bartodziejska2, K. Zych2, A. Rozalski2, and Z. Sidorczyk2
1Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninskii pr. 47, Moscow 119991, Russia; fax: (095) 135-5328; E-mail: knirel@ioc.ac.ru2Institute of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Lodz, Banacha 12/16, 90-237 Lodz, Poland; fax: (48) 42-6784932; E-mail: zsidor@biol.uni.lodz.pl
* To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Received March 11, 2002; Revision received April 16, 2002
Four new Proteus O-specific polysaccharides were isolated by mild acid degradation from the lipopolysaccharides of P. penneri 28 (1), P. vulgaris O44 (2), P. mirabilis G1 (O3) (3), and P. myxofaciens (4), and their structures were elucidated using NMR spectroscopy and chemical methods. They were found to contain non-carbohydrate organic acids, including ether-linked lactic acid and amide-linked amino acids, and the following structures of the repeating units were established:
where (S)-Lac and (R)-aLys stand for (S)-1-carboxyethyl (residue of lactic acid) and Nepsilon-[(R)-1-carboxyethyl]-L-lysine (“alaninolysine”), respectively. The data obtained in this work and earlier serve as the chemical basis for classification of the bacteria Proteus.
KEY WORDS: lipopolysaccharide, O-antigen, bacterial polysaccharide, structure, lactic acid, amino acid, Proteus